Revision Joint Replacement
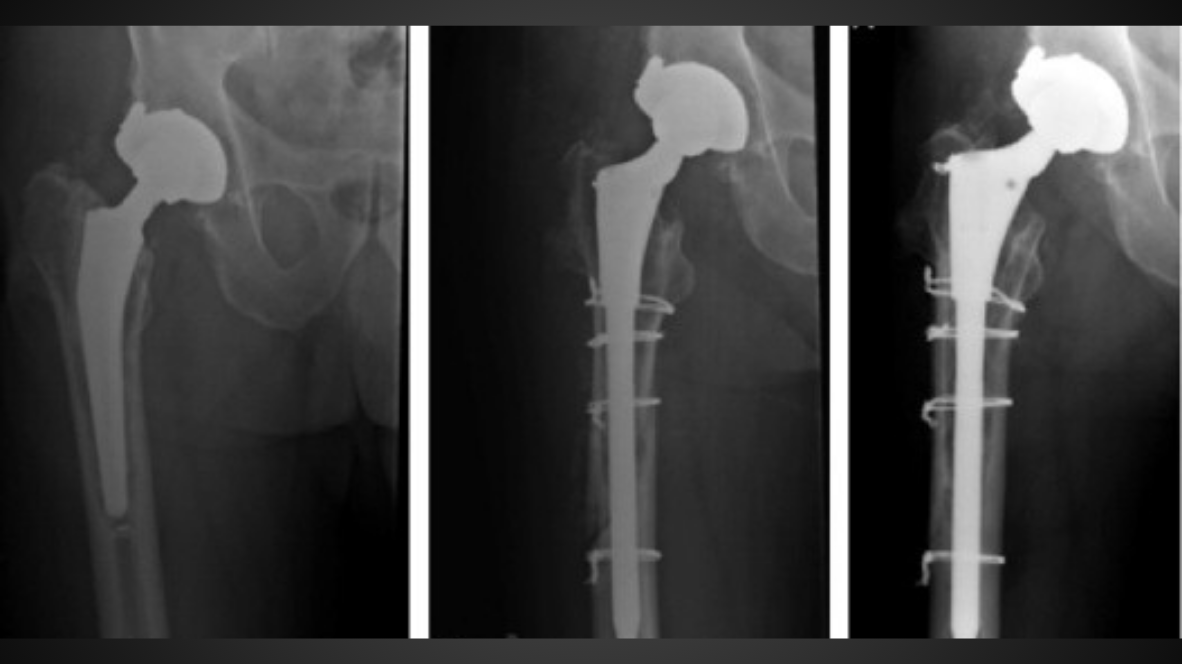
Revision joint replacement is a surgical procedure performed to replace or repair a previously implanted artificial joint that has failed or worn out. It involves removing the old prosthesis and replacing it with a new one to restore function and relieve pain.
Causes:
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the artificial joint components can wear out.
- Loosening of the Prosthesis: The bond between the bone and the implant may weaken.
- Infection: An infection around the artificial joint can necessitate revision surgery.
- Fractures: Bone fractures around the implant.
- Dislocation: Recurrent dislocation of the artificial joint.
- Osteolysis: Bone loss around the implant due to the body’s reaction to wear particles.
Symptoms:
- Pain: Persistent or worsening pain in the joint.
- Swelling: Increased swelling around the joint.
- Instability: Feeling that the joint is giving way or is unstable.
- Decreased Function: Reduced range of motion and difficulty performing daily activities.
- Signs of Infection: Redness, warmth, fever, and drainage from the joint.
Diagnosing:
- Physical Examination: Assessing joint function, pain, and signs of infection.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays: To check for loosening, wear, and positioning of the implant.
- CT or MRI Scans: Detailed images to assess bone quality and the condition of the surrounding tissues.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Blood tests to detect signs of infection or inflammation.
- Joint aspiration to analyze fluid from the joint for infection.
Treatment Options:
- Non-Surgical Management (if appropriate):
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Physical Therapy: To improve strength and function.
- Bracing: To provide support and stability.
- Surgical Options:
- Partial Revision: Only part of the prosthesis is replaced.
- Complete Revision: The entire implant is replaced.
- Bone Grafting: To address bone loss and provide support for the new implant.
Prevention Tips:
- Regular Follow-Ups: Routine check-ups to monitor the condition of the joint replacement.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the joint.
- Avoid High-Impact Activities: Limiting activities that can cause excessive wear on the joint.
- Infection Prevention: Prompt treatment of any infections and maintaining good hygiene.
- Strengthening Exercises: Regular exercises to keep the muscles around the joint strong.
