Robotic Surgery
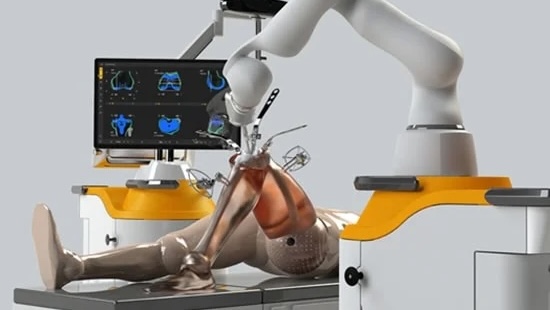
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, involves the use of robotic systems to aid surgeons in performing complex procedures with precision, flexibility, and control. The surgeon operates the robot via a console, which translates their hand movements into precise actions of the robotic instruments.
Causes:
Robotic surgery is used for various medical conditions where traditional surgery is indicated, including:
- Cancer: Prostate, kidney, colorectal, and gynecological cancers.
- Cardiac Conditions: Valve repairs, coronary artery bypass.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Gallbladder removal, hernia repair.
- Urological Problems: Prostatectomy, kidney surgeries.
- Gynecological Procedures: Hysterectomy, myomectomy.
Symptoms:
Symptoms leading to robotic surgery depend on the underlying condition and can vary widely:
- Pain: Persistent or severe pain in affected areas.
- Dysfunction: Issues with organ function, such as urinary problems in urological conditions.
- Masses or Tumors: Detected via imaging or physical examination.
- Bleeding: Abnormal or excessive bleeding in certain conditions.
Diagnosing:
Diagnosis involves identifying the underlying condition requiring surgery:
- Physical Examination: To assess the affected area and overall health.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds to visualize the problem.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Blood tests, urine tests, or biopsies to diagnose and evaluate the condition.
Treatment Options:
- Robotic Surgery Benefits:
- Precision: Enhanced accuracy in surgical procedures.
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, and quicker recovery.
- Enhanced Visualization: 3D high-definition view of the surgical area.
- Reduced Pain and Scarring: Less post-operative pain and smaller scars.
- Surgical Procedures:
- Various procedures across specialties can be performed using robotic systems, offering improved outcomes and shorter hospital stays.
Prevention Tips:
Preventive measures are related to the underlying condition:
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine medical check-ups for early detection of issues.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking.
- Screenings: Regular screenings for cancers and other conditions based on risk factors.
