Spotting and periods are both types of vaginal bleeding, but they are not the same. Understanding the difference between the two can help you track your menstrual health better, identify potential concerns, and decide when to consult a healthcare provider.
This guide will break down the key differences, causes, and treatments for spotting and periods to help you understand your body better.
What is Spotting?
Spotting refers to light vaginal bleeding that occurs outside of your regular menstrual cycle. It is usually minimal and does not require a full sanitary pad or tampon. Spotting may appear as pink, red, or brown discharge and is typically not accompanied by the heavier flow seen during periods.
Common Causes of Spotting
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can cause light bleeding.
- Ovulation: Some women experience spotting mid-cycle when the ovary releases an egg.
- Birth Control Pills: Starting, stopping, or missing doses of birth control can trigger spotting.
- Pregnancy: Implantation bleeding can occur early in pregnancy when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining.
- Infections: Certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) or vaginal infections may cause spotting.
- Stress and Lifestyle Factors: Intense stress, poor diet, and sudden weight changes can contribute to spotting.
- Medical Conditions: Endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or uterine fibroids may lead to spotting.
- Post-Menopausal Bleeding: In older women, spotting may indicate hormonal shifts or other underlying issues.
What is a Period?
A period is the natural shedding of the uterine lining that occurs during a menstrual cycle. Periods generally follow a predictable pattern and involve moderate to heavy bleeding that lasts between 3 to 7 days.
Common Causes of Menstrual Bleeding
- Natural Menstrual Cycle: The hormonal cycle regulates the buildup and shedding of the uterine lining.
- Birth Control Withdrawal: Certain hormonal birth control methods may alter your menstrual flow.
- Perimenopause: Women nearing menopause may experience changes in their period’s duration and intensity.
Key Differences Between Spotting and Periods
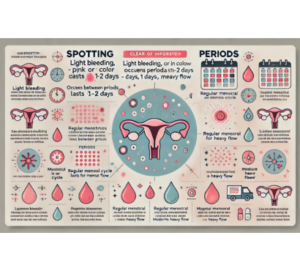
| Feature | Spotting | Periods |
| Flow | Light, may not require a pad | Moderate to heavy, needs a pad/tampon |
| Duration | Usually short (1-2 days) | Lasts 3-7 days |
| Timing | Occurs randomly between cycles | Happens once per menstrual cycle |
| Color | Light pink, brown, or dark red | Bright red to dark brown |
| Accompanying Symptoms | Rarely causes cramps or discomfort | Commonly associated with cramps, bloating, and fatigue |
When to See a Doctor
While occasional spotting may not be a concern, consult a doctor if you experience:
- Spotting for more than a few days without explanation
- Spotting that occurs frequently or becomes heavier
- Bleeding accompanied by severe pain, dizziness, or fatigue
- Postmenopausal spotting
- Spotting after sexual intercourse
Diagnosis of Spotting and Period Issues
Your doctor may perform the following to diagnose the cause:
- Pelvic Exam: To check for infections or growths.
- Ultrasound Imaging: To examine the uterus, ovaries, and other reproductive organs.
- Blood Tests: To assess hormone levels or detect conditions like thyroid issues.
- Pap Smear: To screen for cervical abnormalities or infections.
Treatment for Spotting
Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Birth control or hormone therapy may regulate your cycle.
- Infections: Antibiotics or antifungal medications may be prescribed.
- Lifestyle Changes: Managing stress, improving diet, and ensuring adequate sleep can help reduce spotting.
Treatment for Period Problems
For painful or irregular periods, your doctor may recommend:
- Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen.
- Hormone Therapy: Birth control pills or hormonal IUDs may stabilize your cycle.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, stress management, and a balanced diet can improve menstrual health.
Preventing Spotting and Period Irregularities
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
- Eat a nutrient-rich diet with plenty of iron, calcium, and vitamins.
- Manage stress through yoga, meditation, or mindfulness techniques.
- Track your menstrual cycle using period-tracking apps.
- Attend routine gynecological check-ups for preventive care.
FAQ
1. How can I tell if I’m spotting or starting my period?
Spotting is lighter, shorter, and may occur outside your usual menstrual cycle. Periods involve heavier bleeding, often lasting 3-7 days, and commonly cause cramping.
2. Can stress cause spotting?
Yes, stress can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to spotting between cycles. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can help.
3. Is spotting a sign of pregnancy?
Spotting can be an early sign of pregnancy, especially if it occurs around the time of implantation. If you suspect pregnancy, consider taking a test for confirmation.
